Diamond Cut
What Is A Diamond Cut?
A diamond cut is a style or design guide used when shaping a diamond for polishing such as the brilliant cut. Cut does not refer to shape (pear, oval) but the symmetry, proportioning and polish of a diamond. The cut of a diamond greatly affects a diamond's brilliance; this means if it is cut poorly, it will be less luminous.
A quality cut diamond allows a diamond to express its natural sparkle and scintillation. Cut refers to the quality of a diamond's proportions and symmetry. These angles allow the diamond to capture light and reflect it, producing sparkle. If a diamonds pavilion is too deep, for example the center will be noticeably dark. If you want a truly brilliant diamond, consider those with cut grades of Very Good or Ideal.

A Diamond's Cut Unleashes It's Light
Diamonds are renowned for their ability to transmit light and sparkle so intensely. We often think of a diamond cut as a shape ( round, heart/oval/marquise, pear), but a diamond's cut grade is really about how well a diamond's frets interact with light.
Precise artistry and workmanship are required to fashion a stone so its proportions, symmetry, and polish deliver the magnificent return of light only possible in a diamond.
A diamonds cut is crucial to the stone's final beauty and value. And of all the diamond 4C's, it is the most complex and technically difficult to analyze.
To determine the cut grade of the standard round brilliant diamond - the shape that dominates the majority of diamond jewelry - GIA calculates the proportions of those facets that influence the diamond's face up appearance. These proportions allow GIA to evaluate how successfully a diamond interacts with light to create desirable visual effects such as :
BRIGHTNESS Internal and external white light reflected from a diamond.
FIRE The scattering of white light into all the colors of the rainbow.
SCINTILLATION The amount of sparkle a diamond produces, and the pattern of light and dark areas caused by reflections within the diamond.
GIA's diamond cut grade also takes into account the design and craftsmanship of the diamond, including its weight relative to its diameter, its girdle thickness ( which affects its durability), the symmetry of its facet arrangement, and the quality of polish on those facets.
GIA's diamond Cut Scale for standard round brilliant diamonds in the D - Z diamond color range contains 5 grades ranting from Excellent to Poor.

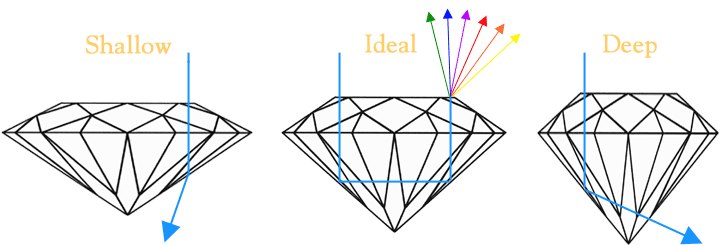
How Does Pavilion Depth Affect A Diamond's Cut?
The distance from the bottom of the girdle to the cult is the pavilion depth. A pavilion depth that's too shallow or too deep will allow light to escape from the side of the stone or leak out of the bottom. A well-cut diamond will direct more light through the crown.
IDEAL CUT - Tremendous sparkle. Excellent polish and symmetry.
VERY GOOD - Lots of sparkle. Great polish and symmetry.
GOOD - A good amount of sparkle. Sufficient polish and symmetry.
POOR - Will not sparkle very much. Unsatisfactory polish and symmetry.
The term "cut" has two references: One is the diamond's shape, the other is the quality, determined by its proportions, symmetry and polish.
The top-selling diamond cut shape is the round brilliant. Other cut shapes including princes, marquise, pear, heart, oval, emerald, radiant, cushion and Asscher are considered fancy cut.
The cut of a diamond is considered to be the most important factor with respect to its beauty. The cut determines the brilliance of the diamonds - how light is reflected, dispersed and scintillated. Unlike color and clarity, there is not a single grade that defines it. Furthermore, two diamonds equal in carat weight, color and clarity can differ in appearance and value because of differences in cut quality.
The cut is the most complicated of the 4Cs. Unlike carat weight, color and clarity, whose value and rarity are related to the diamond's natural formation, cut quality is the result of human decision and diamond cutting skills.

These are three factors that determine a diamond's cut quality:
PROPORTIONS - The relative sizes and angles of the diamond's parts and facets.
SYMMETRY - The precision of the cut design, especially the facets.
POLISH - The smoothness and luster of the diamond's surface.
The cut grades are referenced on a diamond's certificate often using the GIA standards of Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair and Poor. For the most part, the actual measurements are mainly on the laboratory reports.
The quality of a diamond's cut always speaks for itself.
